Cancer Epigenetics Therapy Market By Therapy Type (DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors (DNMTi), Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi), Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors, Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Inhibitors, Others), By Application (Solid Tumors, Hematological Cancers, Others), By Route of Administration (Oral, Injectable), By End-user (SSS1, SSS2, SSS3), Global Market Size, Segmental analysis, Regional Overview, Company share analysis, Leading Company Profiles And Market Forecast, 2025 – 2035
Published Date: Jun 2025 | Report ID: MI2965 | 217 Pages
What trends will shape this market in the coming years?
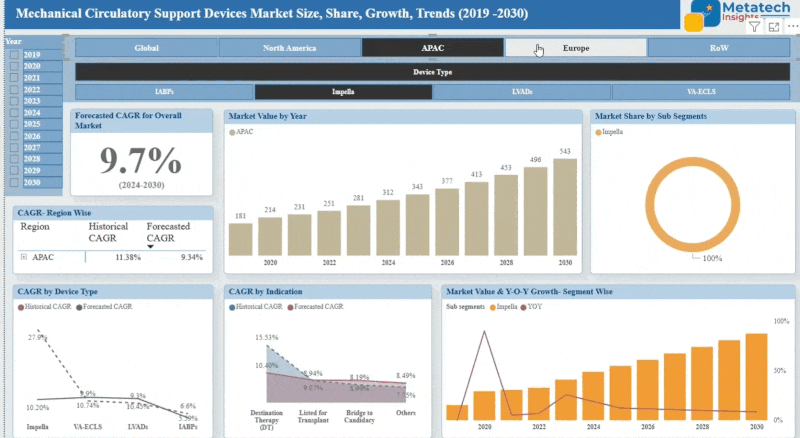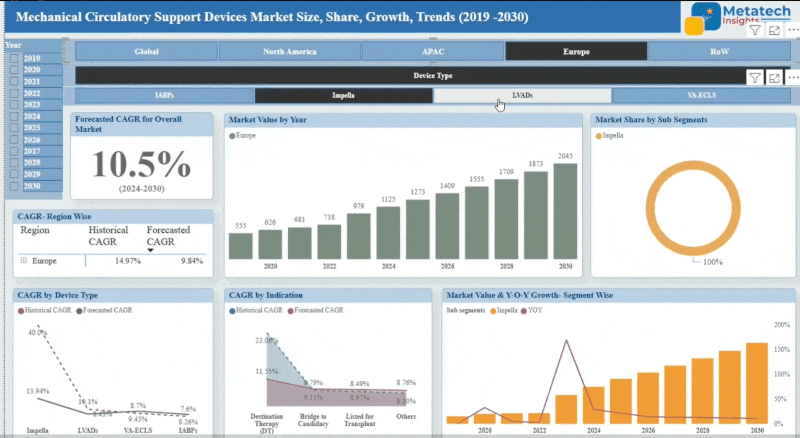
The Cancer Epigenetics Therapy market accounted for USD 14.67 Billion in 2024 and USD 16.93 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 70.9 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 15.4% between 2025 and 2035. The Cancer Epigenetics Therapy Market targets therapies that correct the expression of genes that are abnormal in the cancer cells in a way that does not modify the sequence of genes. Oncogenes are expressed by epigenetic changes, either by silencing of tumor-suppressor genes or activating oncogenes that lead to cancer progression. As compared to gene mutations, these modifications are reversible and thus are the best targets of therapeutics.
Examples of epigenetic therapies are the DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTi) and histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), previously approved on hematologic malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma. They react by unlocking silent genes or changing chromatin architecture in order to block the growth of cancer cells. New drugs also act on bromodomain proteins and histone methyltransferases, which provide further alternatives to solid cancer and resistant cancer.
What do industry experts say about the market trends?
“Each cell in our body has a designated function. The epigenome controls the DNA in every cell… In the case of cancer, cells grow out of control. We are finding that the role of the epigenome is extremely important in determining whether cells will continue to function as intended or become uncontrollable.”
- Prof. Johnathan R. Whetstine, Ph.D. – Cancer Epigenetics Program Leader, Fox Chase Cancer Center
Which segments and geographies does the report analyze?
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 14.67 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2035) | 15.4% |
| Forecast Years | 2025-2035 |
| Historical Data | 2018-2024 |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 70.9 Billion |
| Countries Covered | U.S., Canada, Mexico, U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, Sweden, Finland, Netherlands, Poland, Russia, China, India, Australia, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Brazil, Argentina, GCC Countries, and South Africa |
| What We Cover | Market growth drivers, restraints, opportunities, Porter’s five forces analysis, PESTLE analysis, value chain analysis, regulatory landscape, pricing analysis by segments and region, company market share analysis, and 10 companies. |
| Segments Covered | Therapy Type, Application, Route of Administration, End-user, and Region |
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
What are the key drivers and challenges shaping the market?
Rising cases of AML and MDS are fueling demand for DNMT and HDAC inhibitors.
The outbreak of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) is one of the leading factors that are contributing to the growth of the cancer epigenetics therapy market, especially in boosting demand by DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitors and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. Such blood cancers have a close correlation with epigenetic aberrations; thus, they are good candidates for epigenetically directed therapy. Treatment methods such as DNMT inhibitors, such as azacitidine and decitabine, as well as HDAC inhibitors such as vorinostat, are already extensively utilized in treating such ailments.
Clinical use and commitment to R&D have been on the rise in these classes of drugs as the population of patients requiring targeted, less toxic therapy has been rising. Based on national data provided by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), AML cases have been on the increase, with an estimated 20,380 new cases in 2023 alone in the U.S. Due to the increased attention towards early treatment and disease management, epigenetic therapies are becoming a crucial part of hematologic oncology treatment, boosting the market.
Growth in epigenetic biomarkers allows precise patient targeting, improving treatment efficacy.
The increase in epigenetic biomarkers provides a strong impetus to the cancer epigenetics therapeutics market since the introduction of such biomarkers allows clinicians to target their therapeutics to patients who can get the most benefit. Such biomarkers as DNA methylation patterns, histone alteration permits clinicians to classify patients, assess the responsiveness to therapy, and personalize epigenetic medicines in a more precise manner.
Consequently, the clinical performance is enhanced, resistance is reduced, and healthcare systems are led to confidence concerning the integration of these therapies. A recent report published by an industry player shows that more than 70 percent of current oncology-based research efforts now take into account to establishment of personalized treatment approaches. This thermogenesis in biomarker-based strategies underscores the fact that more funds are being thrown in precision oncology, and thus in the fast track of DNMT and HDAC inhibitors into the clinical environment and leading to the expansion of the market.
Unwanted changes in gene expression can lead to toxicities and limited use.
The threat of undesired alteration of gene expression may be seen as one of the most significant limitations in the cancer epigenetics therapy market since it may trigger off-target effects and toxicities. Because epigenetic therapies are generally broad, as opposed to being specific as with mutation-specific therapy, there is the possibility that epigenetic therapy will inadvertently drive the growth of oncogenes in healthy cells or turn off critical genes. This may cause side effects such as cytopenias, fatigue, or gastrointestinal problems, which also restrict their safe application in some patients.
These adverse effects have been related to unintended consequences that present concerns both to the clinician and the regulators, which often result in limited approvals or combination strategies necessary to achieve the point of safety equilibrium. These issues demonstrate the significance of the creation of more selective epigenetic medicines and the better selection of patients. Risks of toxicity will limit the use of such therapies until more accuracy is obtained.
Offers potential for precise, gene-specific, long-term epigenetic reprogramming.
One of the significant market opportunities faced by the cancer epigenetics therapy market is related to the establishment of accurate, gene-specific, and long-lasting epigenetic reprogramming. New technologies such as CRISPR-based epigenome editing and targeting of small molecules have the potential to fine-tune gene expression without the DNA sequence. This forms the capability of long-lasting reactivation of cancer-suppressing genes or forced silence of oncogenes with little off-target.
This accuracy would have the effect of providing a far more effective therapeutic effect and less toxicity. Inherent to long-term reprogramming, it could also reduce the episodes of relapses by providing the cancer cells with a stable epigenetic profile. With the further development of research, these innovations can be used to change the treatment strategies and apply epigenetic therapy not only to hematologic cancer but also to solid tumors. This trend unlocks the path to more personal and efficient cancer treatment.
An untapped market, as epigenetic dysregulation plays a role in several childhood cancers.
The less developed potential of treating childhood cancers with epigenetic dysregulation is a major opportunity in the cancer epigenetics therapy market. Numerous cancer diseases in children (neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma, some leukemia) have no major genetic mutations, but contain changes in DNA methylation and histone modification. This qualifies them as candidates for an epigenetic therapy. Nevertheless, the majority of existing therapies are happening to adults, so there is a gap in developing child-specific drugs.
Improving research on the nature of epigenetic targets most suitable in different ages, as well as safe dosing, may open up novel horizons of therapy for this vulnerable group. The growing attention to rare and pediatric cancers on the global health agenda, as well as in research organizations, also fosters this opportunity, which may go a long way in enhancing outcomes for young patients and developing the market as well.
What are the key market segments in the industry?
Based on the Therapy type, the Cancer Epigenetics Therapy market has been classified into DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors (DNMTi), Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi), Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors, Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Inhibitors, and Others. DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors (DNMTi) are the most dominant in the Cancer Epigenetics Therapy Market. These inhibitors will act on the silencing of tumor suppressor genes through DNA methylation, which is an important mechanism playing a role in epigenetic silencing. DNMT inhibitors prevent the action of the DNA methyltransferase enzymes so that these genes can be reinvigorated and regain their normalcy to check on tumor growth.
Some of the currently approved DNMT inhibitors (including azacitidine and decitabine) have demonstrated a substantial clinical efficacy, especially in the treatment of hematological malignancies, such as myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML). This segment is the most dominant due to its proven therapeutic value, early regulatory strengths, as well as its extensive use in the oncology practice. Moreover, their recent studies demonstrated that DNMT inhibitors are related to combination therapies and, thus, this fact further reinforces the position within the cancer treatment arena.
Based on the application, the Cancer Epigenetics Therapy market has been classified into Solid Tumors, Hematological Cancers, and Others. Hematological Cancers is the most predominant segment under application in the Cancer Epigenetics Therapy Market. Epigenetic therapies have demonstrated the greatest success in managing blood disorders like acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and lymphoma. AZA, decitabine, vorinostat, and romidepsin are already approved specifically in these conditions and commonly used in treatment schemes.
Blood cancers are more optimistically considered to be epigenetically regulated because they interact directly with the circulating cells and the easily available bone marrow habitats, making drug delivery and monitoring an easy task. Also, the demand of targeted and combination epigenetic therapies in this segment has been due to extensive clinical research, prior regulatory approvals, and high relapse rates of these cancers, consequently making it the most active application segment.
Which regions are leading the market, and why?
The North American cancer epigenetics therapy market is in a dominant position as the market is loaded with head strength in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries, superior healthcare infrastructure, and high R&D investments. The US is ahead of the region regarding FDA-approved epigenetic drugs, such as the DNMT and HDAC inhibitors, such as azacitidine, decitabine, and vorinostat. The lead research centers and institutes focused on cancer treatment, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, are actively involved in Next-generation epigenetic therapies clinical trials.
The area enjoys a considerable level of awareness of the precision medicine culture, as well as easy affinity to biomarker tests, making it possible to stratify patients and employ precision epigenetics therapy measures. Market growth is aided by an increase in hematologic cancer prevalence and a positive reimbursement policy. Other factors that speed up approvals of new epigenetic drugs are orphan drug designations and regulatory support in rare cancers. Besides, academia-industry collaborations help to promote innovation and accelerate the transformation of research into treatments.
The Asia-Pacific cancer epigenetics therapy market is also a rapidly increasing sector, due to the expanding cancer burden, healthcare infrastructure, and the growing influence of governments on offering cancer care. The targeted cancer agents, such as DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors, have shown an increased demand in countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India. Epigenetic drugs are new kinds of alternative medicines, and governments like the NMPA of China have started to approve them, as has been the case with TAZVERIK (r-tazemetostat) in follicular lymphoma.
The increasing investment in the sector of biotechnology, as well as the growing clinical research networks, is helping in the local development and testing of epigenetic drugs. Moreover, the area also has an extensive patient pool and increased attention to personalized treatment and biomarker-based medication. The partnerships between international pharma companies and Asian firms are growing and provide the countries with the possibility to get access to innovative therapies in a shorter period. In spite of their weaknesses, such as difficulties in treatment affordability and access disparities among the countries, the Asia-Pacific region positions itself as a land of opportunities and high industry growth potential in the market of cancer epigenetics therapy.
What does the competitive landscape of the market look like?
The cancer epigenetics therapeutic market is very competitive, with a combination of large pharmaceutical firms and a number of specialized biotech firms. Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis are the key players that have very strong pipelines and strategic alliances. These corporations are concentrated on widening their product range through purchases and collaborations to preserve their top position in the market. As an illustration, the acquisition of Celgene by Bristol-Myers Squibb greatly enhanced its epigenetic capabilities. Innovation by biotech companies such as Epizyme, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, and Oryzon Genomics provides niche-focused technologies such as EZH2 inhibitors and HDAC inhibitors.
Their dexterity and research orientation enable them to develop new treatment methods through clinical trials in a very short time. Also, most of these companies partner with academic institutions to access the emerging epigenetic targets. Combination therapies are also developed, which quite obviously influence the competitive environment, because epigenetic drugs are combined with immunotherapies or chemotherapies to be more effective. Businesses are moving towards the development of next-generation sequencing and the development of biomarkers to better select patients and affect patient therapeutic dynamics.
Cancer Epigenetics Therapy Market, Company Shares Analysis, 2024
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
Which recent mergers, acquisitions, or product launches are shaping the industry?
- In March 2025, HUTCHMED’s TAZVERIK® (tazemetostat) received conditional approval from China’s NMPA for treating relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma with EZH2 mutations. The drug, developed in collaboration with Epizyme, marks a key advancement in epigenetic cancer therapy in Asia.
Report Coverage:
By Therapy Type
- DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors (DNMTi)
- Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi)
- Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors
- Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Inhibitors
- Others
By Application
- Solid Tumors
- Hematological Cancers
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Injectable
By End-user
- Hospitals
- Cancer Research Institutes
- Specialty Clinics
- Others
By Region
North America
- U.S.
- Canada
Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
List of Companies:
- Epizyme, Inc.
- Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Constellation Pharmaceuticals
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Novartis AG
- Eisai Co., Ltd.
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- AbbVie Inc.
- Roche Holding AG
- Oryzon Genomics
- Celleron Therapeutics
- Celgene Corporation
- Astex Pharmaceuticals
- Chroma Therapeutics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Cancer Epigenetics Therapy market accounted for USD 14.67 Billion in 2024 and USD 16.93 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 70.9 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 15.4% between 2025 and 2035.
Key growth opportunities in the Cancer Epigenetics Therapy market include Offers potential for precise, gene-specific, long-term epigenetic reprogramming, an Untapped market as epigenetic dysregulation plays a role in several childhood cancers, improving patient compliance, and expanding treatment accessibility.
The largest segment is DNMT inhibitors in hematological cancers, and the fastest-growing segment is BET inhibitors in solid tumors.
North America leads, driven by strong R&D, FDA approvals, and advanced healthcare infrastructure boosting market growth.
Leading players include Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Merck & Co., GSK, AbbVie, Epizyme, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, and Oryzon Genomics.
Maximize your value and knowledge with our 5 Reports-in-1 Bundle - over 40% off!
Our analysts are ready to help you immediately.