Lignin-based Biopolymers Market By Product Type (Lignosulfonates, Kraft Lignin, Organosolv Lignin, Soda Lignin, Hydrolysis Lignin, Sulfur-free Lignin and Others), By Application (Plastics & Polymers, Binders & Adhesives, Carbon Fiber, Phenolic Resins, Polyurethane (PU) Foams, Films and Coatings and Others), By Processing Technology (Kraft Process, Sulfite Process, Organosolv Process, Enzymatic Hydrolysis, Ionic Liquid Extraction and Steam Explosion), By End-user (Packaging, Automotive, Building & Construction, Electronics, Agriculture and Others), Global Market Size, Segmental analysis, Regional Overview, Company share analysis, Leading Company Profiles And Market Forecast, 2025 – 2035
Published Date: Jun 2025 | Report ID: MI3002 | 210 Pages
What trends will shape this market in the coming years?
The Lignin-based Biopolymers market accounted for USD 1.38 Billion in 2024 and USD 1.44 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 2.27 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 4.61% between 2025 and 2035. The lignin-based biopolymers market is oriented on the production and usage of lignin-based polymers, which are sustainable polymers that are derived from a complex organic polymer known as lignin, which comprises the cell wall of plants and is one of the principal by-products of the pulp and paper industry. These biopolymers are already finding applications as a replacement for the petroleum-based plastics in the packaging, agricultural, auto, and construction industries. Lignin is a potentially very rich and renewable raw material, and it can be used in carbon-neutral products and fuels. The market forces include a rise in environmental concerns and regulations by the government encouraging bio-based materials and technologies of lignin extraction and lignin modification. With lignin-based biopolymers, they are likely to become important to the green materials industry as sustainability becomes essential.
What do industry experts say about the market trends?
"Lignin Industries exists to show another way is possible: that by looking to the natural world, we can positively reform the global plastic industry. Our proprietary process takes an organic material and upcycles it into a sustainable, high‑performance bio‑based thermoplastic."
- Dr. Christopher Carrick, Founder and Chair of the Board at Lignin Industries
"Producing Renol® is resource efficient. Water and land usage is low, there is no competition to food production, and our yield is almost 100% – the only thing lost in the process is some percentage points of water evaporating when run through the extruder."
- Fredrik Malmfors, CEO of Lignin Industries
Which segments and geographies does the report analyze?
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.38 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2035) | 4.61% |
| Forecast Years | 2025-2035 |
| Historical Data | 2018-2024 |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 2.27 Billion |
| Countries Covered | U.S., Canada, Mexico, U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, Sweden, Finland, Netherlands, Poland, Russia, China, India, Australia, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Brazil, Argentina, GCC Countries, and South Africa |
| What We Cover | Market growth drivers, restraints, opportunities, Porter’s five forces analysis, PESTLE analysis, value chain analysis, regulatory landscape, pricing analysis by segments and region, company market share analysis, and 10 companies. |
| Segments Covered | Product Type, Application, Processing Technology, End-user, and Region |
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
What are the key drivers and challenges shaping the market?
Stringent environmental regulations encouraging biopolymer industry adoption worldwide.
Strict environmental regulations in various countries around the world, which have gained much momentum in the recent past, have served as a major impetus for the use of lignin-based biopolymers. The rise of active policies filled with governments to mitigate carbon emission levels and plastic waste has prompted industries to reconsider the production and use of conventional petroleum-based plastics and instead choose to use more sustainable variants.
The Circular Economy Action Plan of the European Union encourages the recycling of plastic packaging, which drives the industries further away from biopolymers, such as lignin. Lignin is another byproduct of the paper and pulp industry that is strong, natural, and easy to obtain. It is renewable and biodegradable, which means that it doesn't depend on fossil fuels as much.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) suggests that bioplastics offer the opportunity to eliminate greenhouse gas emissions when they are used without environmental pollution compared to traditional plastics. Colleges like the University of California, Berkeley, point out the role of lignin in the creation of sustainable and environmentally friendly materials that meet the demands of global sustainable development. A combination of these regulations and environmental aspects is the factor that boosts the demand for lignin-based biopolymers.
Increasing fossil fuel prices boost interest in renewable lignin alternatives.
The rising cost of fossil fuels has made sustainable alternatives a highly marketable concept, which is another major factor driving interest in lignin-based biopolymers. Lignin is a renewable natural polymer based on plant biomass, which can replace petroleum-based plastics and would meet the international objective to decrease carbon footprints. The major growth factors of the lignin-based biopolymers market are rising environmental regulations, consumer education on plastic pollution problems, and processing and modification technologies of lignin.
The Department of Energy of the U.S. estimates that lignin constitutes between 15% and 30% of the dry weight of lignocellulosic biomass, which makes it a rich and affordable raw material. In addition, according to the European Commission, bio-based polymers, such as lignin derivatives, might cut greenhouse gas emissions by as much as 60% when compared to normal (conventional) plastics. Circular economy and green materials are some of the initiatives encouraged by the governments, so lignin-based biopolymers are at the forefront as an essential ingredient in the development of sustainable materials and decarbonising processes.
Technical challenges in processing lignin to consistent polymer quality.
Lignin's structure and variability make it difficult to process effectively into biopolymers of consistent quality. Many distinct phenolic units with various connecting chemical bonds make up the heterogeneous, irregular polymer known as lignin, which varies depending on the plant source and the extraction process. This variation impedes the necessary standardisation in polymer production, leading to variations in the final biopolymer's mechanical and chemical characteristics. Lignin is not thermally or readily soluble, which creates problems in the process of preparation and combinations with other polymers.
The U.S. Department of Energy through its Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy notes that recalcitrance of lignin (measures the degree to which something can be easily altered or changed in terms of chemicals) is one of the greatest challenges in the lignin valorisation process since lignin can be unpredictably reformed or reintegrated into high-performance materials.
Further, scholarly research at establishments like the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) points out that the absence of standardised lignin supply chains and inadequate knowledge about lignin depolymerisation processes hinder scalability and marketability. A combination of these conditions hampers the development of the lignin-based biopolymers market, and they require further research to find a way to control the modification of lignin and to reproduce its properties.
Expanding applications in automotive, textile, agriculture, and construction sectors.
Lignin-based biopolymers represent a sustainable, eco-friendly solution as an alternative to fossil-based plastics in several industries. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that 15-30% of plant biomass is lignin, and the resource is abundant. The structural composites made in the automotive industry will enable the lightweighting of the vehicle, cause fuel efficiency, and minimise emissions, which is coordinated with the EPA objectives.
Lignin possesses natural antioxidant and UV-protective properties, which can be used in the textile industry, encouraging the production of environmentally friendly fibres and dyes, the research of which is conducted even by such academic centres as Cornell University. The USDA is trying to make farming more environmentally friendly by using slow-release fertilisers made from lignin and biodegradable films.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) says that lignosulfonates make concrete stronger and easier to work with when building. These examples show how lignin can be used in many different ways to make materials more sustainable. The government is funding research to find better ways to extract and process lignin on an industrial scale. It makes the biopolymers made from lignin part of the switch to greener industrial processes on Earth.
Collaboration with bio-refineries supports integrated biopolymer production pipelines.
Lignin-based biopolymers have a strong opportunity because commercial industries are switching to renewable sources in the replacement of petroleum-based polymers. Lignin, a large byproduct of bio-refineries and the paper industry, has provided a good source of biopolymers, which are abundant, renewable, and untapped. Lignin can be added to the biopolymer pipelines, which will decrease fossil fuel dependence, minimise environmental impacts, and finally improve the financial success of bio-refineries.
The U.S. Department of Energy reported that 15-30% of lignocellulosic biomass consists of lignin, which has a huge potential as the raw material for producing high-value bioproducts. Another area that the USDA points out is the use of lignin in the production of biodegradable materials that also fits the trend of establishing more laws enforcing the reduction of plastic waste.
Studies conducted in organisations such as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) focus on the use of lignin as an adhesive, composite, and film product as a way to achieve a circular bioeconomy. All these factors put together make lignin-based biopolymers a prospective field with narrowing benefits that are both environmental and economical.
What are the key market segments in the industry?
Based on the product type, the Lignin-based Biopolymers market has been classified into Lignosulfonates, Kraft Lignin, Organosolv Lignin, Soda Lignin, Hydrolysis Lignin, Sulfur-free Lignin, and Others. In the lignin-based biopolymers market, kraft lignin remains a prominent force and a huge segment. It is thus considered the most prominent market due to its wide availability as a by-product of kraft pulping, which is the most common pulping method in the paper and pulp industry. Kraft lignin is usually considered the best type of lignin with fairly high purity and chemical properties that would make it work well in producing several kinds of biopolymers, binders, and composites. Moreover, they are cheap and readily available due to an already-established supply chain, which is a reason for their dominance over types like lignosulfonates or organosolv lignin in the market.
Based on the application, the Lignin-based Biopolymers market has been classified into Plastics & Polymers, Binders & Adhesives, Carbon Fiber, Phenolic Resins, Polyurethane (PU) Foams, Films and Coatings, and Others. The most significant and sizable application fields in the lignin-based biopolymers market are binders and adhesives. Its superiority comes from the binding capabilities of lignin, which allow it to be considered a greener alternative to conventional petroleum-based adhesives. The use of lignin-based adhesives in any commercial building application has created demand for these products in wood products, plywood, and particleboard manufacturing. There is ever-increasing demand for sustainable, bio-based adhesives from diverse industries that further provide impetus for this segment to grow at a faster pace than others, such as plastics or carbon fibre.
Which regions are leading the market, and why?
The North America-based lignin-based biopolymers market continues to sustain steady growth, as environmental consciousness rises and demand for sustainable materials does as well. Equipped with ample lignin availability from the huge forestry and paper industries in the region, manufacturers are now working towards transforming this natural polymer into eco-friendly alternatives for plastics, adhesives, and composites. Modernised technology developments empower product enhancement in terms of performance and pricing to counterbalance petroleum products.
The new and supportive government regulations encouraging reductions in carbon footprint and fostering green chemistry contribute to driving the market growth. The highly developed research infrastructure and the academic-industry partnership further expedite product development and commercial adoption. Yet, inconsistent lignin quality and supply scale act as challenges to acceptance on a wide scale. However, these challenges are doable and could see North America positioned as a leading region to push forward applications of lignin biopolymers in various sectors, including packaging, automotive, and construction.
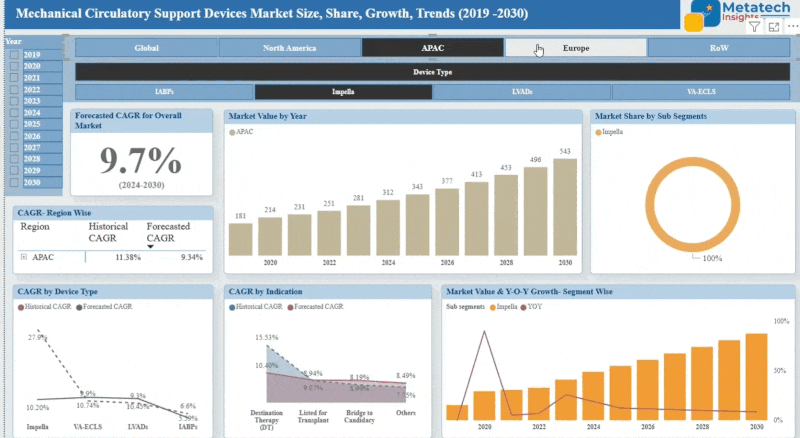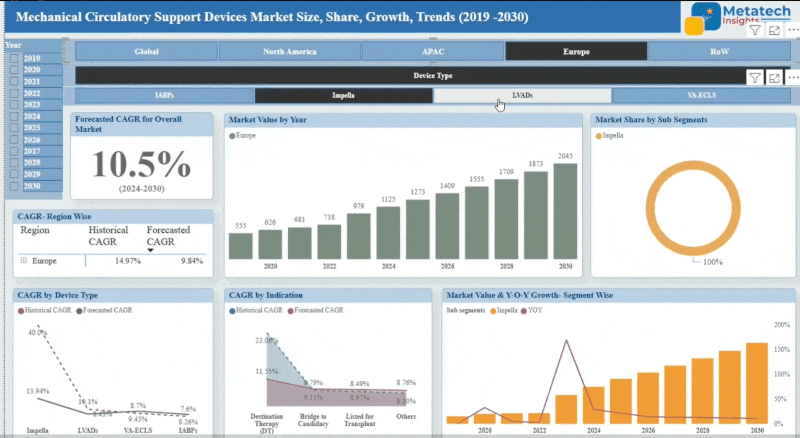
The Asia-Pacific lignin-based biopolymers market is expanding due to increasing environmental consciousness and demand for a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are investing deeply in research and development to use lignin, a natural polymer derived from plant biomass, as a raw material in the formation of biodegradable plastics and composites.
The expanding bio-refinery infrastructure and policies of the respective governments supporting green technologies further provide an impetus to the growth of the market. Moreover, the increasing application of lignin-based biopolymers in packaging, agriculture, and automotive sectors is also driving the demand. Certain constraints, such as the extraordinary cost of production and technical inadequacy, linger. Overall, due to the abundant lignin resource and increasing consumer awareness toward environmentally friendly products, the Asia-Pacific market exhibits promising potential.
What does the competitive landscape of the market look like?
The lignin-based biopolymers market is walking with some mix of established industry giants and new innovators. Other companies such as Borregaard, Stora Enso, UPM, and Sappi are building lignin-based solutions using their market-tested pulp and biorefinery infrastructure at scale. Ingevity and Domtar are putting their concentration into transforming lignin into performance additives and resins that can be used in industries.
In the meantime, incipient companies such as Lignolix and MetGen are also leading breakthroughs in lignin depolymerisation and functionalisation. Most recent partnerships, including the cooperation of UPM with insulation materials to provide lignin-based binder and Vertoro processing bio-oil out of lignin, support the rising interest in bio-based materials in the context of construction and packaging. The European policies in favour of green chemistry also promote the cross-border projects and pilot plants that enhance rivalry and innovation.
Lignin-based Biopolymers Market, Company Shares Analysis, 2024
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
Which recent mergers, acquisitions, or product launches are shaping the industry?
- In March 2025, Lignopure received the prestigious DurchSTARTer Prize 2024 in Lower Saxony. The award recognized their work in transforming raw lignin into high-performance natural ingredients. One of their key products was Lignopure Base™, used in lipsticks, sunscreens, and lotions. This achievement highlighted their innovation in sustainable materials.
- In December 2024, the company finalized an agreement with Hellyar Plastics to introduce Renol to UK markets. After 18 months of testing, they began rolling out Renol-based products. These products targeted both consumer and industrial applications. The partnership marked a significant step in expanding Renol’s market presence.
Report Coverage:
By Product Type
- Lignosulfonates
- Kraft Lignin
- Organosolv Lignin
- Soda Lignin
- Hydrolysis Lignin
- Sulfur-free Lignin
- Others
By Application
- Plastics & Polymers
- Binders & Adhesives
- Carbon Fiber
- Phenolic Resins
- Polyurethane (PU) Foams
- Films and Coatings
- Others
By Processing Technology
- Kraft Process
- Sulfite Process
- Organosolv Process
- Enzymatic Hydrolysis
- Ionic Liquid Extraction
- Steam Explosion
By End-user
- Packaging
- Automotive
- Building & Construction
- Electronics
- Agriculture
- Others
By Region
North America
- U.S.
- Canada
Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
List of Companies:
- Borregaard ASA
- Stora Enso Oyj
- UPM-Kymmene Oyj
- Ingevity Corporation
- Lignolix
- West Fraser Timber Co., Ltd.
- Domtar Corporation
- Aditya Birla Group
- Sappi Limited
- Nippon Paper Industries Co., Ltd.
- Burgo Group S.p.A.
- Rayonier Advanced Materials
- Metsa Group
- Changzhou Shanfeng Chemical Co. Ltd.
- Valmet Corporation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Lignin-based Biopolymers market accounted for USD 1.38 Billion in 2024 and USD 1.44 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 2.27 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 4.61% between 2025 and 2035.
Key growth opportunities in the Lignin-based Biopolymers market include Growing R&D investments for enhancing lignin polymer conversion efficiency, Expanding applications in automotive, textile, agriculture, and construction sectors, and Collaboration with bio-refineries supports integrated biopolymer production pipelines.
The largest and fastest-growing segments in the lignin-based biopolymers market are packaging and automotive due to sustainability demand.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to make a notable contribution to the global lignin-based biopolymers market due to growing industrial demand.
Leading players in the global lignin-based biopolymers market include Borregaard, Stora Enso, UPM Biochemicals, Ingevity, Domtar Corporation, and Domsjö Fabriker (Aditya Birla Group).
Maximize your value and knowledge with our 5 Reports-in-1 Bundle - over 40% off!
Our analysts are ready to help you immediately.