Monoclonal Antibodies in Veterinary Health Market By Product Type (Caninized Monoclonal Antibodies, Felinized Monoclonal Antibodies, Chimeric Monoclonal Antibodies, Bispecific Antibodies, Others), By Application (Pain Management, Dermatology, Infectious Diseases, Oncology, Autoimmune & Inflammatory Diseases, Neurological Disorders, Others), By Mechanism of Action (Anti-inflammatory mAbs, Immunomodulatory mAbs, Targeted mAbs for Pathogen Neutralization, Tumor-Targeting mAbs, Receptor Blockers), By Route of Administration (Intravenous (IV), Subcutaneous (SC), Intramuscular (IM)), By Animal Type (Companion Animals, Livestock Animals, Exotic and Zoo Animals), and By End User (Veterinary Hospitals & Clinics, Academic & Research Institutes, Animal Health Companies, Contract Research Organizations (CROs), Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratories), Global Market Size, Segmental analysis, Regional Overview, Company share analysis, Leading Company Profiles And Market Forecast, 2025 – 2035
Published Date: Jul 2025 | Report ID: MI3023 | 210 Pages
What trends will shape this market in the coming years?
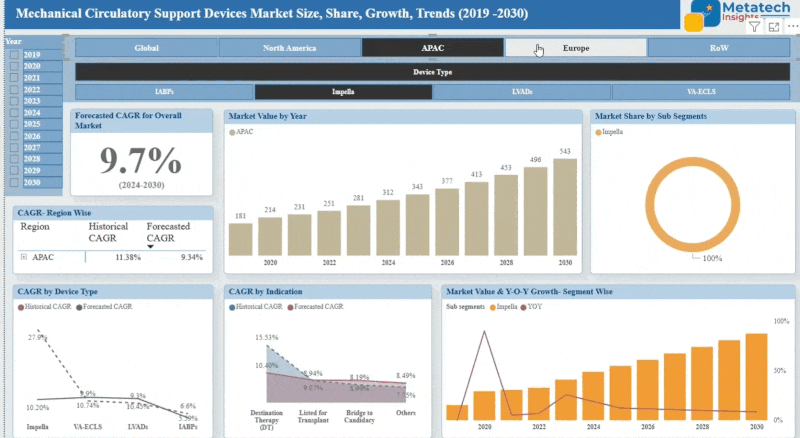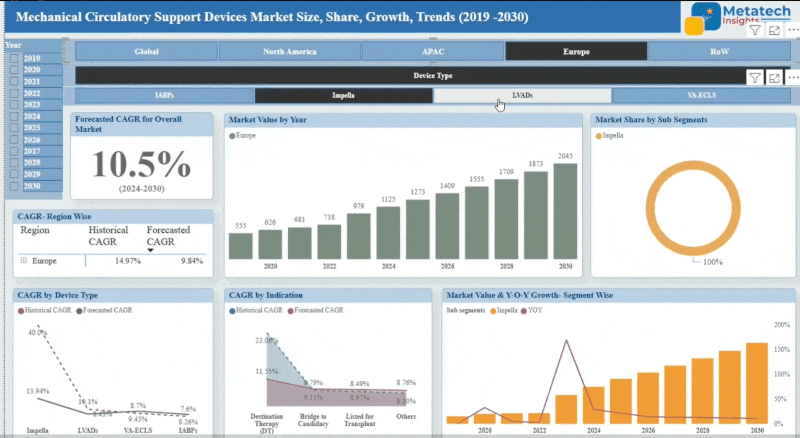
The Monoclonal Antibodies in Veterinary Health market accounted for USD 1.09 Billion in 2024 and USD 1.29 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 5.67 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 17.93% between 2025 and 2035. Monoclonal Antibodies in the Veterinary Health Market deals with the investigation and application of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in the treatment and prevention of animal diseases. They are produced in the laboratory and will target specific antigens that can offer specific treatment against conditions like cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune illnesses in pets or even livestock. Growth in this market is a result of growth in pet ownership, augmented spending in animal healthcare, and progress in biotechnology. It is also driven by regulatory approvals and an increase in awareness concerning targeted therapies. The products covered in the market are companion animal and farm animal products.
What do industry experts say about the market trends?
"Pets are at the center of everything we do at Zoetis... we remain confident in the safety and effectiveness of Librela® and will implement updated U.S. labeling immediately to support veterinarians and pet parents."
- Dr. Richard Goldstein, DVM, DACVIM, Global Chief Medical Officer at Zoetis
"Parvo is a devastating disease... Elanco’s Canine Parvovirus Monoclonal Antibody has achieved a 93% survival rate in real-world usage and reduced hospitalization time by nearly two days."
- Dr. Chris George, Infectious Disease Expert at Elanco Animal Health
Which segments and geographies does the report analyze?
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.09 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2035) | 17.93% |
| Forecast Years | 2025-2035 |
| Historical Data | 2018-2024 |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 5.67 Billion |
| Countries Covered | U.S., Canada, Mexico, U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, Sweden, Finland, Netherlands, Poland, Russia, China, India, Australia, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Brazil, Argentina, GCC Countries, and South Africa |
| What We Cover | Market growth drivers, restraints, opportunities, Porter’s five forces analysis, PESTLE analysis, value chain analysis, regulatory landscape, pricing analysis by segments and region, company market share analysis, and 10 companies. |
| Segments Covered | Product Type, Application, Mechanism of Action, Route of Administration, Animal Type, End User, and Region |
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
What are the key drivers and challenges shaping the market?
Growing awareness of animal diseases fosters monoclonal antibody development.
The increased consciousness about diseases of animals has gained traction as a critical factor that boosted the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) market in veterinary health. With the rise in threats posed by infectious diseases on livestock and companion animals, quick and accurate diagnosis and proper treatment play an essential role in controlling the large-scale breakout of the disease and resulting financial losses.
The sensitivity and specificity of monoclonal antibodies mean they can be used both as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool in veterinary practice. In the report by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), animal health problems, such as bovine respiratory disease and mastitis, are major causes of financial burden, and more complex interventions are required.
The Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) emphasises that enhancing animal health has a direct contribution to food security and livelihoods all over the world. The vision of managing diseases and animal welfare has increased, which drives investment in mAbs to resolve points and eventually counter traditional therapies. Use of monoclonal antibodies can therefore be considered in line with the world in improving animal health and productivity, as well as animal biosecurity.
Technological advances enhance antibody production efficiency and clinical effectiveness.
Increasing demand for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in veterinary health is mainly due to the necessity of specific diagnostics and precision treatment in the aim of enhancing the health and productivity of animals. There have been developments in technology, particularly in the methods of production of antibodies, i.e., the recombinant DNA technology and the use of hybridoma methods, which have greatly increased the efficiency and the specificity of the process of producing antibodies.
The innovation enables the production of mAbs that are capable of targeting infectious agents, cancers, and autoimmune diseases in animals and decreases the use of antibiotics and the success of treatment. There is further penetration of monoclonal antibody-based products in veterinary care due to the awareness of zoonotic diseases and stringent measures on the health of animals. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) estimates that infectious diseases are the top cause of economic losses in the livestock industry and places an emphasis on the need to establish better therapeutic options.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) highlight the contribution of monoclonal antibodies to the progression of human and animal health due to the offering of specific immunotherapies, thus reiterating their increasing relevance in veterinary practices.
High development costs limit accessibility in small veterinary practices.
The elevated rates of development tend to limit the availability of monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatments more in small veterinary practices. These biologics are complicated in research, intricate production facilities, and tight regulatory approval, and they add to the cost of production. Such treatments are often expensive and infrastructurally demanding and thus are only available to bigger or special veterinary clinics.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reports that the biologics sector, in which mAbs fall, entails long-term development processes with an average of 10-15 years, and the costs of bringing a single product can run up to hundreds of millions of dollars. Further, the Centre of Veterinary Biologics (USDA) indicates that safety and efficacy testing should be highly rigorous, increasing the time and cost of entry into the market. This mix of high initial capital cost and regulation limits the ability of smaller vet practices to adopt monoclonal antibody therapy, which filters through to wider access for animal patients.
Expanding livestock health programs open doors for antibody innovation.
The use of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is one of the emerging areas of veterinary health, especially as the focus in disease management in livestock turns to selective, anti-antibiotic therapies. Governmental agencies with support funds, such as the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) at the USDA, sponsor various programs that favour mAb generation in cattle, pigs, and poultry to resist pathogens like E. coli, rotavirus, and PEDV. In one example, at Texas A&M, researchers have developed recombinant antibodies that have helped prevent calf diarrhoea by inhibiting the attachment of pathogens, which led to the major cause of neonatal mortalities.
Further, Washington State University has developed several hundred species-specific antibodies to facilitate diagnostic and vaccine development in food animals. An approvable species-specific biologics example is a conditionally licensed canine parvovirus mAb at the USDA, an indication of regulatory progress toward mAbs in animal health. With increased national momentum to curb antimicrobial resistance (AMR), the antibody innovations stand in good shape to deliver economically and environmentally sustainable production of livestock, leading to better herd immunity and less dependence on drugs.
Strategic partnerships boost research funding and global market reach.
A major opportunity to increase the application of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in the veterinary health market comes through strategic alliances in the corner of the market. This has been true in companion animals, where monoclonal antibodies also provide targeted treatment options for conditions such as cancer, osteoarthritis, and allergies. The USDA states that the number of pet owners in the U.S. is also on the increase, with more than 70% of the households owning pets, thus necessitating the need to have more advanced types of treatment.
Regulatory support for such innovation is already present, as the Centre for Veterinary Medicine of the FDA has already approved mAbs such as Cytopoint. Moreover, the negative impact of zoonotic diseases on the global population stimulates the development of interest in cross-species biologics under the support of such frequently mentioned research institutions as NIH and WHO that promote the voices of the so-named approach of One Health. These elements present a productive soil through which biotech firms, universities, and veterinary pharmaceutical companies can work together in developing and commercialising mAbs all over the world.
What are the key market segments in the industry?
Based on the product type, the Monoclonal Antibodies in Veterinary Health market has been classified into Caninized Monoclonal Antibodies, Felinized Monoclonal Antibodies, Chimeric Monoclonal Antibodies, Bispecific Antibodies, and Others. Canine monoclonal antibodies represent the most conspicuous part of the veterinary monoclonal antibodies market. These are designed specifically to fit the dogs, which causes minimal immune rejection, according to which treatment outcomes can be further improved. The prevalence of caninised antibodies is fuelled by the strong demand for effective therapy of the common canine disorders, such as osteoarthritis and atopic dermatitis. Other products, such as the species-specific Cytopoint and Librela, have also recorded a high adoption rate in animal health practices. Caninised mAbs are a dominant power in these markets because their clinical effectiveness, safety record, and commercial realisation have been confirmed.
Based on the application, the Monoclonal Antibodies in Veterinary Health market has been classified into Pain Management, Dermatology, Infectious Diseases, Oncology, Autoimmune & Inflammatory Diseases, Neurological Disorders, and Others. Among the application sectors in the veterinary monoclonal antibodies market, dermatology can be regarded as the strongest one. Skin conditions, especially atopic dermatitis in dogs, are one of the most commonly treated health problems that are treated in veterinary clinics. Treatment with monoclonal antibodies such as Cytopoint has revolutionized the management of itching and inflammation by providing a specific, non-reducing, long-term itch and inflammation attack and has a lower side effect profile than conventional treatments. Dermatology is the most popular application in the market due to the high incidence of dermatology and the effectiveness of mAbs in treating conditions in the field.
Which regions are leading the market, and why?
The North American monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in veterinary health market have massive growth due to the growing animal health awareness and the demand for high-end biologics in the companion and farm animal treatment market. The area has a good veterinary healthcare system, pet ownership, and government policies that favour control of animal diseases. Key industry giants in biotechnology and animal health are putting their money into research to come up with species-specific mAbs in diseases such as cancer, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
The United States dominates the market with its well-built regulation system and a high rate at which it adopts novel therapeutics. Partnerships between veterinary practices, research labs, and medicine companies are helping accelerate the development of products. The livestock sector is also catching up, with producers trying to find viable tools in disease management to help them improve their productivity. With the emergence of precision medicine, North America will continue to be characterised as one of the main centres of veterinary monoclonal antibody research and development.
The Asia-Pacific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in veterinary health market are growing due to increased awareness in animal health and investment in livestock productivity. India, China, Japan, and Australia lead the pack as the increasing market demands state-of-the-art disease prevention methods and treatment services. Rapid growth of the middle-income population and pet population in the region also stimulates the demand for veterinary therapeutics.
Government programmes that maintain the well-being of the animals in terms of healthcare facility development and surveillance of disease are developing the market. Partnerships between local biotech companies and international companies are making the local manufacturing and innovation better. But the cost of production and the regulatory nature continue to be problems. The Asia-Pacific environment will grow steadily, which is due to the technological acceptance and the growing interest in animal welfare.
What does the competitive landscape of the market look like?
The competition in the monoclonal antibodies in veterinary health market is changing very fast, as big pharmaceutical firms are in it, and small biotechnology firms. Zoetis continues to be a leader, with the advantage of being the first mover and obtaining regulatory approval of mAb-based drugs in companion animals. The increasing biologics pipeline at Merck Animal Health indicates that the company plans to enter the immunotherapy solution market. Elanco is also stepping up with targeted advancement in the treatment of infectious diseases through mAbs. There is also competition caused by the entry into the long-acting antibody product field using small but innovative businesses such as Invetx (now Dechra Pharmaceuticals).
Virbac and Ceva Sant Animal are getting progressively involved as far as collaborating and purchasing businesses to expand their biologics portfolio. A lot of partnerships in the biotech industry and academic centres have not been the exception as the companies strive to conquer chronic and acute pet diseases by developing specific immunotherapies. There is a lot of strategic research and development, licensing deals, and pre-commercial foul play in the market, mainly in North America and Europe, where the need for precision veterinary treatment is growing.
Monoclonal Antibodies in Veterinary Health Market, Company Shares Analysis, 2024
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
Which recent mergers, acquisitions, or product launches are shaping the industry?
- In June 2025, Elanco’s Canine Parvovirus Monoclonal Antibody (CPMA) received conditional approval from the USDA. It was allowed for use as passive immunity in puppies exposed to parvovirus. The treatment showed effectiveness in shelters across Florida. Elanco supported this with a $200 rebate and a free-sample program.
- In April 2025, Virbac secured a license from Japan’s MabGenesis to develop veterinary monoclonal antibodies for canine diseases. The agreement included licensing fees, milestone payments, and royalties. It aimed to expand Virbac’s molecular product portfolio in the veterinary field.
Report Coverage:
By Product Type
- Caninized Monoclonal Antibodies
- Felinized Monoclonal Antibodies
- Chimeric Monoclonal Antibodies
- Bispecific Antibodies
- Others
By Application
- Pain Management
- Dermatology
- Infectious Diseases
- Oncology
- Autoimmune & Inflammatory Diseases
- Neurological Disorders
- Others
By Mechanism of Action
- Anti-inflammatory mAbs
- Immunomodulatory mAbs
- Targeted mAbs for Pathogen Neutralization
- Tumor-Targeting mAbs
- Receptor Blockers
By Route of Administration
- Intravenous (IV)
- Subcutaneous (SC)
- Intramuscular (IM)
By Animal Type
- Companion Animals
- Livestock Animals
- Exotic and Zoo Animals
By End User
- Veterinary Hospitals & Clinics
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Animal Health Companies
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratories
By Region
North America
- U.S.
- Canada
Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
List of Companies:
- Zoetis
- Merck & Co.
- Elanco Animal Health
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Indian Immunologicals Ltd
- Virbac
- Bayer AG
- Dechra Pharmaceuticals
- Advio GmbH
- Kindred Biosciences
- Ceva Santé Animale
- Aratana Therapeutics
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Sanofi S.A.
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Monoclonal Antibodies in Veterinary Health market accounted for USD 1.09 Billion in 2024 and USD 1.29 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 5.67 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 17.93% between 2025 and 2035.
Key growth opportunities in the Monoclonal Antibodies in Veterinary Health market include Expanding livestock health programs open doors for antibody innovation, Emerging economies show demand for modern animal disease treatments, and Strategic partnerships boost research funding and global market reach.
The largest segment is companion animals; fastest-growing is livestock due to rising disease prevention needs and increased monoclonal antibody adoption in farming.
North America will make a notable contribution due to advanced veterinary infrastructure, strong R&D investment, and high awareness of animal health treatments.
Leading players include Zoetis, Merck Animal Health, Elanco, Boehringer Ingelheim, Virbac, Indian Immunologicals, Bayer Animal Health, Ceva Santé Animale.
Maximize your value and knowledge with our 5 Reports-in-1 Bundle - over 40% off!
Our analysts are ready to help you immediately.