Oncogenic Signaling Market By Targeted Signaling Pathway (mTOR Pathway Inhibitors, β-Catenin Pathway Inhibitors, Notch Signaling Pathway Inhibitors, Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Inhibitors, and Others), By Molecule Type (Small Molecule Inhibitors, Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs), RNA-based Therapeutics, and Cell-based Therapies), By Cancer Type (Lung Cancer, Breast Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Leukemia, Lymphoma, and Others), By Biomarker Type (Genomic Biomarkers, Proteomic Biomarkers, Transcriptomic Biomarkers, and Epigenetic Biomarkers), By Therapeutic Approach (Targeted Therapy, Combination Therapy, Personalized Therapy, and Immuno-Oncology Synergistic Therapy), and By End User (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, Academic & Research Institutes, Cancer Research Centers, Hospitals & Clinics, and Contract Research Organizations), Global Market Size, Segmental analysis, Regional Overview, Company share analysis, Leading Company Profiles And Market Forecast, 2025 – 2035
Published Date: Jun 2025 | Report ID: MI3008 | 220 Pages
What trends will shape this market in the coming years?
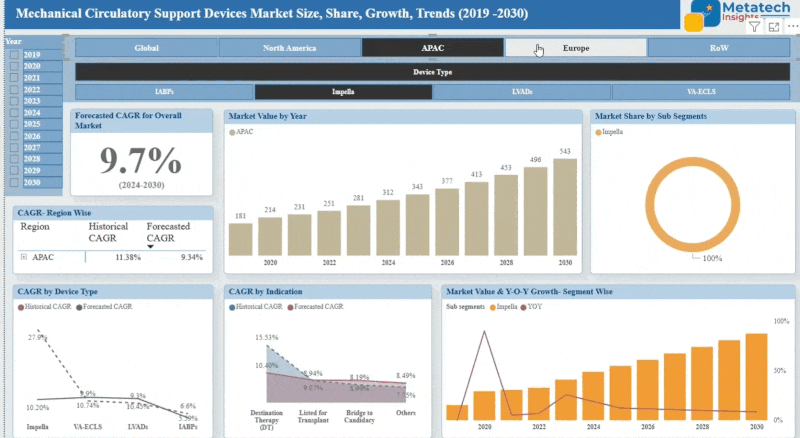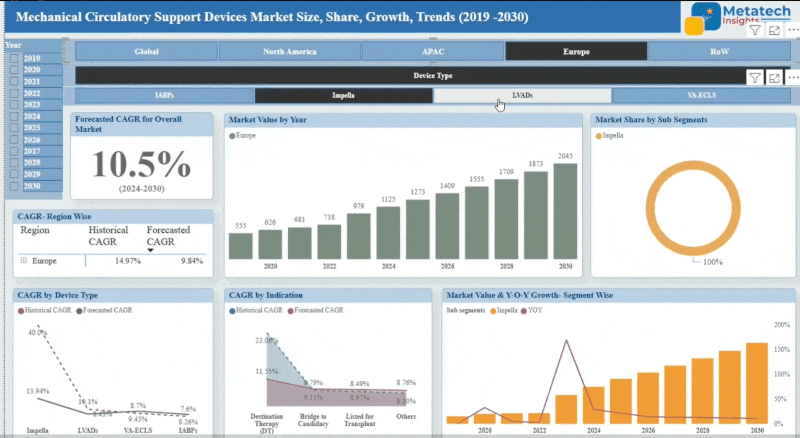
The Oncogenic Signaling market accounted for USD 72.4 Billion in 2024 and USD 80.5 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 232.7 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 11.2% between 2025 and 2035.The oncogenic signalling market is developing the therapy framework and diagnostic equipment countering oncogenic signalling pathways, which are the main accelerators of cancer development and progression. Such signalling pathways have molecular processes that favour out-of-control cell multiplication and the occurrence of tumours. There are drugs, inhibitors, and technologies that are used to block or desensitise these pathways to treat different cancers in the market. The market is growing with growth in the prevalence of cancer, the growth in molecular biology, and the growth in personalised medicine. It is a very significant field in the sphere of oncology that works on making the outcomes of the treatments positive, working on the fundamentals of cancer at the cellular signalling level.
What do industry experts say about the market trends?
"RT11-i represents a breakthrough: this cell-penetrating antibody directly targets activated RAS proteins intracellularly, inhibiting downstream oncogenic cascades and overcoming resistance in tumor models."
- Dr. Yong Sung Kim, Co‑founder of Orum Therapeutics
"The BRAF team at IRIC successfully restored normal conformational control of mutant BRAF using small molecules, showcasing a novel route to shutting off oncogenic MAPK signaling in cancer."
- Marc Therrien, CEO & Director of IRIC Intracellular Signaling Research Unit
Which segments and geographies does the report analyze?
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 72.4 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2035) | 11.2% |
| Forecast Years | 2025-2035 |
| Historical Data | 2018-2024 |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 80.5 Billion |
| Countries Covered | U.S., Canada, Mexico, U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, Sweden, Finland, Netherlands, Poland, Russia, China, India, Australia, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Brazil, Argentina, GCC Countries, and South Africa |
| What We Cover | Market growth drivers, restraints, opportunities, Porter’s five forces analysis, PESTLE analysis, value chain analysis, regulatory landscape, pricing analysis by segments and region, company market share analysis, and 10 companies. |
| Segments Covered | Targeted Signaling Pathway, Molecule Type, Cancer Type, Biomarker Type, Therapeutic Approach, End User, and Region |
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
What are the key drivers and challenges shaping the market?
Rising cancer prevalence increases demand for targeted oncogenic signaling therapies.
The expanding cancer incidence worldwide is a primary growth factor for demand in oncogenic signalling markets. WHO listed cancer as a common cause of death worldwide, with 19.3 million new cases and almost 10 million deaths estimated in 2020. With an increase in the incidence, the need for increased effective treatment strategies and personalised treatment options is essential. Driving oncogenic signalling pathways for tumour growth and progression has attracted treatment targets for novel cancer therapies.
Governments and research organisations NCI and others stress that targeted therapies critically improve outcomes in inhibiting molecular drivers of cancer. Targeted signalling pathway inhibitors have received greater acceptance and development due to precision medicine, supported by extensive genomic research. Given the rising cancer incidence, especially in ageing populations, considerable future demand for these targeted therapies would provide robust support for ongoing innovations and investments in the oncogenic signalling market.
Growing investments in oncology research fuel development of innovative drugs.
Cancer is witnessing a rise in prevalence, hence a huge push for therapies that interfere with abnormal signalling pathways relating to tumour growth and metastasis. Molecular biology further created a better understanding of oncogenic pathways like EGFR, PI3K/AKT, and RAS/RAF/MEK and thereby further advanced drug development with a focus on binding targets that come in the way of these processes.
According to WHO, cancer brought about nearly 10 million deaths worldwide in the year 2020, indicating therapies. Furthermore, according to the National Cancer Institute, about 39.5% of people will be diagnosed with cancer at some point in their lifetime in the U.S., signifying a vast patient population requiring novel therapeutic interventions. The increased support for cancer research by government agencies as well as academic institutions provides momentum to ongoing drug discoveries and clinical trials, and promotes market growth for oncogenic signalling.
Complex signaling pathways challenge effective drug design and clinical translation.
A lot of intricacy in oncogenic signal transduction pathways becomes a constraint that hinders targeted therapy development and clinical translation in the oncology market. These pathways may bear many feedback loops, cross-talk occurring between different signalling cascades, and compensatory mechanisms wherein cancer cells can elude single-agent treatments. Such biological complexity makes drug target identification that would otherwise be effective across diverse tumour types difficult. The NCI states that resistance mechanism-based therapies and tumour heterogeneity remain some of the biggest obstacles to treating cancer, as many of whom relapse as an adaptive response to signalling.
The FDA confirms that a small percentage of oncology drugs entering clinical trials ultimately get approved, reflecting the problem with translating molecular insight into therapies that work and have lasting effects. This clearly illustrates the need for a better understanding of the signalling network and the development of combination therapies to improve clinical outcomes in the oncogenic signalling market.
Expansion in emerging markets creates untapped demand for cancer therapeutics.
The emerging markets offer a promising entryway to oncogenic signalling, given the rising numbers of cancer patients and the improving structure of healthcare in these economies. While ageing populations, urbanisation, and lifestyle modifications have been causing an increase in the number of cancer patients in the Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and African regions, there remains a huge unmet medical demand since about 70% of cancer deaths happen in low- and middle-income countries (WHO).
Intensified attention by the governments in these regions toward health gives impetus to the enhancement of cancer diagnosis and treatment facilities and creates demand for targeted therapies that work via inhibition of oncogenic signalling pathways. For instance, the NCI states that the research and funding for molecular-targeted cancer therapies are ever-expanding. In this rapidly transforming environment, biopharmaceuticals with new oncogenic signalling inhibitors find huge service in uplifting the potential for patient care, promising in these under-provided populations.
Combination therapies with immuno-oncology agents offer new treatment paradigms.
Combination therapies combining immuno-oncology agents thus present a major growth opportunity for the oncogenic signalling segment by improving efficacy against some cancers and overriding resistance mechanisms. Oncogenic signalling is involved in tumour cell survival, but many pathways may operate simultaneously in a tumour. Therefore, by blocking multiple pathways simultaneously, combinations can improve patient survival. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) mentions that immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with targeted therapies have shown promise for some cancers, including non-small cell lung carcinoma and melanoma, where germline or somatic mutations in certain genes are implicated in disease progression.
The American Cancer Society states that cancers with mutations in some of the key oncogenic pathways, such as EGFR, BRAF, and PI3K, are among the common ones and therefore form an ideal group of cancers for a combination approach. The FDA approval of various combination regimens involving immuno-oncology agents and targeted inhibitors signifies an increased clinical and regulatory interest. This changing paradigm lays the foundation for novel drug development and novel treatment strategies to address unmet needs and expand market size.
What are the key market segments in the industry?
Based on the Targeted Signaling Pathway, the Oncogenic Signaling market has been classified into mTOR Pathway Inhibitors, β-Catenin Pathway Inhibitors, Notch Signaling Pathway Inhibitors, Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Inhibitors, and Others. In the signalling pathways targeted in the oncogenic signalling market, mTOR inhibitors maintain a position of supreme importance. The mTOR pathway governs cell growth, proliferation, and survival. It is a principal driver in many cancers. Therefore, the mTOR has taken centre stage in tumour initiation and mechanisms of resistance to therapy, with mTOR inhibitors then receiving enormous clinical attention with several FDA approvals of therapies and an extremely strong research pipeline in place. Their application across various cancer types and the near-universal efficacy of mTOR inhibitors against tumours certainly propels them to the forefront of market interests against any other types of pathway inhibitors.
Based on the Molecule Type, the Oncogenic Signaling market has been classified into Small Molecule Inhibitors, Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs), RNA-based Therapeutics, and Cell-based Therapies. Small-molecule inhibitors are the biggest and foremost segment in oncogenic signalling markets. These inhibitors easily enter cells and interfere with intracellular signalling processes to suppress key oncogenic drivers. Hence, from the convenience of oral administration, favourable cost of manufacture, and applicability to a wide set of cancer indications, these small molecules stand on different advantageous shores. The larger number of approved small-molecule drug cases and the wider commercial pipeline for drug candidates confer this segment with a higher strategic prominence among targeted cancer therapies over other molecule types like monoclonal antibodies or RNA-based therapeutics.
Which regions are leading the market, and why?
The North American oncogenic signalling market is experiencing strong growth because of rising cancer cases and the development of molecular diagnostics. Healthcare infrastructure is very strong, and research funding and the presence of major pharmaceutical firms working on the development of targeted cancer drugs provide a great advantage to the region. The increasing knowledge regarding personalised medicine and early recognition is increasing the demand for oncogenic signalling inhibitors as well as diagnostic products. Moreover, joint ventures of biotech companies and universities speed up industrial development in this field.
The US is the largest market, whose adoption is leading because there are established regulatory environments and reimbursement structures. Increased investments in oncology research and development help to expand the pipeline further. Nevertheless, excessive prices of treatment and elaborate regulatory issues still pose a problem. North America is a powerful and flourishing centre of therapeutic strategies and diagnostics, which could be used as an oncogenic disturbance.
The Asia-Pacific oncogenic signalling market is one of the fastest-growing markets, which is attributed to the rising cancer prevalence and awareness of targeted therapies in the region. Investments made in healthcare infrastructure and sophisticated diagnostic units are on the increase in countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India, putting them at the forefront of the demand. The availability of precision medicine and the government efforts to encourage research on cancer and its treatment also contribute to the development of the market.
Improved biotechnology and the growth in the research collaborations of local and foreign pharmaceutical organisations are enhancing the creation of new oncogenic signalling blockers. Nevertheless, development might be hampered by factors like low accessibility in rural regions and high treatment prices. Asia Pacific is quite promising in terms of market players, as it has a large population base of patients, and continuous efforts are being made in cancer therapeutics.
What does the competitive landscape of the market look like?
The oncogenic signalling market is highly competitive, with large biopharmaceutical players throwing their weapons in all directions in a bid to expand their targeted therapy pipeline. Universal participants like Merck & Co., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Roche, AstraZeneca, and Novartis are switching to next-generation inhibitors that attack vital cancer pathways, including KRAS, BRAF, and PI3K. Recent transactions, including Bristol-Myers Squibb and BioNTech, with a billion-dollar deal in bispecific antibodies, can illustrate how much the sector is focused on combination mechanisms that enable it to conquer resistance.
The investment of Merck in the technology of discovering antigens indicates the tendency to precision on the molecular level. The acquisition of a licensed PRMT5 inhibitor by Bayer demonstrates how the company is changing the paradigm of synthetic lethality-based treatments. Other than expansion via R&D, companies are expanding via strategic alliances and acquisitions, signalling that this is a long-term strategy to emerge on top of this high-potential segment of oncology.
Oncogenic Signaling Market, Company Shares Analysis, 2024
To explore in-depth analysis in this report - Request Sample Report
Which recent mergers, acquisitions, or product launches are shaping the industry?
- In May 2025, BioNTech announced that it had scheduled presentations at ASCO. The company presented its anti‑PD‑L1×VEGF‑A bispecific antibody, BNT327. It also showcased select antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) programs. These programs aimed to modulate intracellular signaling in cancer treatment.
- In May 2025, Eli Lilly shared updates on olomorasib at ASCO. The drug is a second-generation KRAS G12C inhibitor. Preliminary data showed activity in the central nervous system (CNS). It also showed promising combination results with pembrolizumab in NSCLC and cetuximab in CRC.
Report Coverage:
By Targeted Signaling Pathway
- mTOR Pathway Inhibitors
- β-Catenin Pathway Inhibitors
- Notch Signaling Pathway Inhibitors
- Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Inhibitors
- Others
By Molecule Type
- Small Molecule Inhibitors
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
- RNA-based Therapeutics
- Cell-based Therapies
By Cancer Type
- Lung Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Others
By Biomarker Type
- Genomic Biomarkers
- Proteomic Biomarkers
- Transcriptomic Biomarkers
- Epigenetic Biomarkers
By Therapeutic Approach
- Targeted Therapy
- Combination Therapy
- Personalized Therapy
- Immuno-Oncology Synergistic Therapy
By End User
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Cancer Research Centers
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Contract Research Organizations
By Region
North America
- U.S.
- Canada
Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
List of Companies:
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- Roche Holding AG
- AstraZeneca plc
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Amgen Inc.
- Sanofi S.A.
- Bayer AG
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- BeiGene, Ltd.
- Incyte Corporation
- Seattle Genetics, Inc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Oncogenic Signaling market accounted for USD 72.4 Billion in 2024 and USD 80.5 Billion in 2025 is expected to reach USD 232.7 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 11.2% between 2025 and 2035.
Key growth opportunities in the Oncogenic Signaling market include Emerging biomarkers enable personalized medicine for precise oncogenic signaling targeting, Expansion in emerging markets creates untapped demand for cancer therapeutics, and Combination therapies with immuno-oncology agents offer new treatment paradigms.
The largest segment is breast cancer; the fastest-growing is lung cancer due to rising incidence and demand for targeted oncogenic signaling therapies.
North America will make a notable contribution due to advanced healthcare, strong research funding, and high adoption of targeted oncogenic signaling therapies.
Pfizer, Roche, AstraZeneca, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, AbbVie, Seagen, Takeda dominate global oncogenic signaling market.
Maximize your value and knowledge with our 5 Reports-in-1 Bundle - over 40% off!
Our analysts are ready to help you immediately.